For loop in Excel VBA
The VBA for loop is used to execute the group of statements for the given number of times. The for loop should be used if you know how many times a loop will run in advance.

The VBA for loop is used to execute the group of statements for the given number of times.
For example, you have ten cells in an Excel sheet and are required to read the numeric value in each cell and multiply by 10 or apply a formula.
You may use a For..Next loop to iterate through each cell (from 1 to 10).
On each iteration, multiply the cell value by 10 ( or perform any other desired action) and assign the result to the second column cells.
I will show you examples of that let us first look at the syntax of the for loop.
- 1. Structure of using for..Next loop
- 2. An example of displaying numbers in an Excel sheet by using for loop
- 3. An example decrementing the counter
- 4. An example of Fahrenheit to Celsius with for loop
- 5. A demo of using nested for loop
- 6. The example of omitting the current iteration - Continue alternate
- 7. Using the exit statement in for loop VBA
Structure of using for..Next loop
Following is the general syntax of using the for loop in Visual Basic for Applications:
For counter = start To end [ Step step ]
[code/statements to execute here]
Next [ counter ]
Where:
| Part | Description |
| Counter | The Counter is the numeric variable that is required. |
| Start | The Start sets the initial value of the Counter variable. |
| End | The End specifies the end value.
As the counter reaches this value, the loop should be terminated. |
| Step | Step defines the value of the Counter variable incremented or decremented in each iteration. |
| Code | You may place a group of statements to be executed on each iteration. |
| Next | The Next keyword is required that terminates the definition of the for loop. |
| Exit | If you require exiting the loop at any stage, use the Exit statement. |
The for loop should be used if you know in advance how many times a loop will run.
An example of displaying numbers in an Excel sheet by using for loop
In the following example, a for loop is used to display the numbers from 1 to 10 to the ten cells in the A column. Have a look:
Private Sub for_loop_Click() Dim x As Integer For x = 2 To 10 Step 1 Cells(x, 1).Value = x Next x End Sub
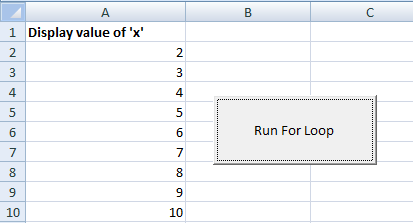
This is how the for loop worked in the example:
- You can see, the for loop code is written in the click event of the ActiveX button.
- The button is placed on the Excel sheet. In the for loop, the initial value of the counter variable is set as 2.
- The step is 1, so x will be incremented by 1 on each iteration of the loop.
- This line of code will update the excel cell by the value of x:
- The first cell in the Excel sheet is given the heading text.
- The Next x statement incremented the value of x by 1. As long as the value of x was less than or equal to 10, the loop continued. As it reached the value 11, the condition became false and for loop terminated.
An example decrementing the counter
In this example, the value of the counter is decremented on each iteration of the for loop.
The initial value of the Counter variable x = 100.
In each iteration, it is decremented by 10. The current value of the Counter variable is set in the Excel cell like the above example:
Private Sub for_loop_Click() 'Demo of decrementing counter variable Dim x As Integer, y As Integer y = 2 For x = 100 To 10 Step -10 Cells(y, 1).Value = x y = y + 1 Next x End Sub
The output:
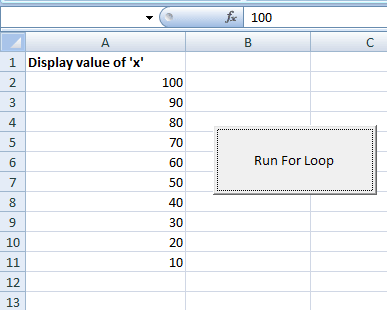
The value of x is displayed from 100 to 10 with a gap of 10 in Excel cells.
An example of Fahrenheit to Celsius with for loop
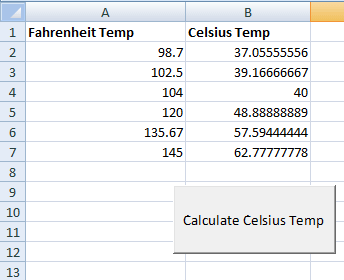
The cells in column A (2 to 7) contain the Fahrenheit temperatures while the adjacent cell in column B is empty initially.
As the button is pressed, the for loop will execute and take the values of Fahrenheit temperatures. The Fahrenheit to Celsius formula is applied in each iteration.
The result is updated on the related cell in column B. Following is the program:
Private Sub for_loop_Click() 'Example of Fahrenheit to Celsius with for loop For x = 2 To 7 Step 1 Cells(x, 2).Value = (5 / 9) * (Cells(x, 1).Value - 32) Next x End Sub
A demo of using nested for loop
In this case, the inner loop is executed for each iteration of the outer for loop.
Have a look at the code below to learn more about this:
Private Sub for_loop_Click() 'The nested loop example Dim i As Integer, j As Integer, k As Integer k = 2 'Out For i = 2 To 16 Step 3 For j = 1 To 3 Step 1 Cells(k, 2).Value = j k = k + 1 Next j Cells(i, 1).Value = i j = 2 Next i End Sub
The output of the code:
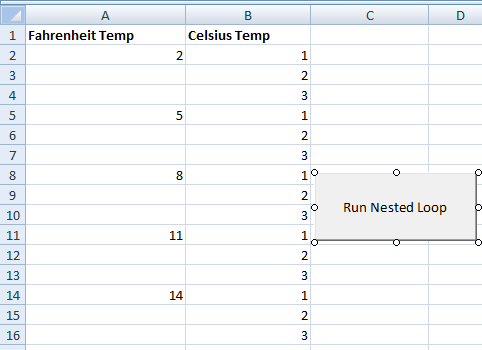
There,
- The outer loop updates column A’s specified cell by the variable i’s value.
- The inner loop iterates three times and updates the cells by 1,2,3.
- The loop goes on till the value of the variable i reaches 16.
The example of omitting the current iteration - Continue alternate
VBA has no continue statement which is used to omit current iteration in various programming languages.
If you require omitting the current iteration, you may use different solutions for that.
One of the solutions is shown in the example below. A for loop is supposed to run from numbers 2 to 11 with an increment of 1 on each iteration of the loop.
The current value will be updated on the Excel sheet, however, for values 3,5, and 7 the loop will omit the current iteration without updating the Excel cell.
Have a look:
Private Sub for_loop_Click() Dim x As Integer For x = 2 To 10 Step 1 If x = 3 Or x = 5 Or x = 7 Then 'Nothing to execute Else Cells(x, 1).Value = x End If Next x End Sub
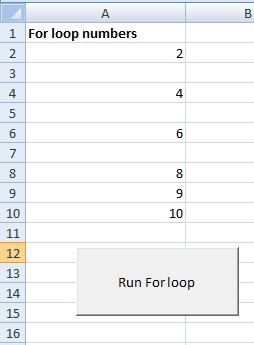
Using the exit statement in for loop VBA
As mentioned earlier, use the Exit For statement to eliminate the loop and move the execution next line after the For loop.
See the usage of Exit For in the following example:
Private Sub for_loop_Click() Dim x As Integer For x = 2 To 10 Step 1 If x = 5 Then 'Ending the for loop and exeuction moves to the next line after loop Exit For Else Cells(x, 1).Value = x End If Next x End Sub
The result:
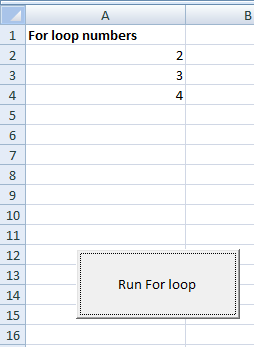
You saw that the loop was supposed to run until the value of x reached 10, however, it ended as it reached 5 by using the Exit For statement.