How to Create and Access Arrays in Excel VBA
How to create arrays in VBA by using different ways. Accessing array elements by index. One-dimensional and two definitional arrays (using Excel Sheet)
VBA Arrays and ExcelIn this tutorial, you will learn:
- How to create arrays in VBA by using different ways
- Accessing array elements by index
- One-dimensional and two definitional arrays (using Excel Sheet)
- A few useful array methods
- 1. How to declare arrays in VBA
- 2. An example of creating, assigning, and accessing array elements
- 3. The second way of creating and accessing arrays
- 4. An example of specifying the start and end index in the array
- 5. Iterating through each element of the array by For..Each
- 6. Using LBound and UBound functions to get array length
- 7. An example of creating a 2D array based on Excel cells
- 8. Displaying a whole two-dimensional array
How to declare arrays in VBA
First Way to create arrays
- Declare it first by using the Dim keyword like any other variable.
- Size of the array in parenthesis
- The data type of the array
For example
This will create an array of five elements.
Second way:
So, provide the index position of the elements.
In that case, an array of four elements from 2 to 5 index is created.
An array can also be created as simply as it:
Dim arr
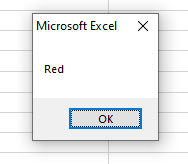
An example of creating, assigning, and accessing array elements
In this example,
- We will declare a string array of five elements.
- Then we will assign values to elements by index numbers.
- Finally, we will access the third element value in a message box.
Have a look:
VBA code:
Sub Arrays_ex() 'Declaring an array of five elements starting at 0 Dim arr_colors(4) As String 'Creating array elements arr_colors(0) = "Black" arr_colors(1) = "White" arr_colors(2) = "Red" arr_colors(3) = "Green" arr_colors(4) = "Orange" 'Accessing array element MsgBox arr_colors(5) End Sub
Output:
The second way of creating and accessing arrays
We are creating an array without specifying the size and data type.
VBA code:
Sub Arrays_ex()
Dim Langs
'Creating an array of four elements
Langs = Array("C#", "Java", "C++", "Python")
'Display second element of the array
MsgBox Langs(1)
End Sub
Output:
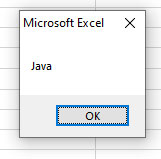
An example of specifying the start and end index in the array
In this example, we are creating an array of fixed size by specifying the start and end index numbers at the time of declaration (as shown in the syntax above).
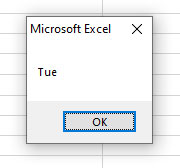
We will give 2 to 6 index numbers as below:
Sub Arrays_ex() 'Declaring an array from 2 to 6 index Dim arr_day(2 To 6) As String 'Creating array elements arr_day(2) = "Tue" arr_day(3) = "Wed" arr_day(4) = "Thu" arr_day(5) = "Fri" arr_day(6) = "Sat" 'Accessing array element MsgBox arr_day(2) End Sub
Output:
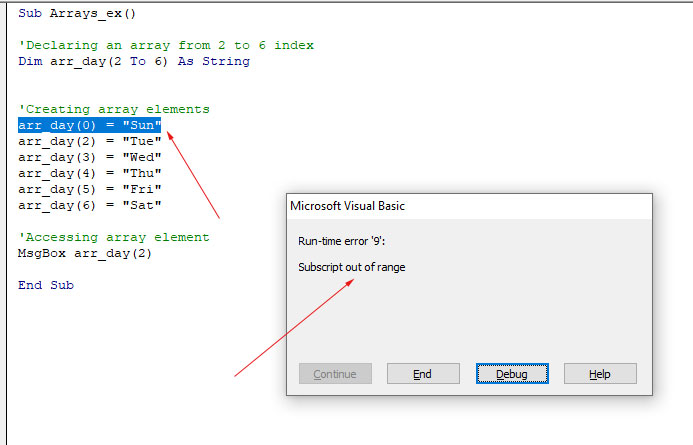
If you provide 0 index then the following error occurs, like arr_day(0) = “Sun”:
Iterating through each element of the array by For..Each
In the example below,
- We have an array of five elements.
- We will iterate through each array element,
- and collect its values in a string variable.
- After the loop ends, we will display all array elements with concatenation and linebreak:
VBA Code:
Sub Arrays_ex() 'Declaring an array of five elements starting at 0 Dim arr_colors(4) As String Dim CollAll As String 'Creating array elements arr_colors(0) = "Black" arr_colors(1) = "White" arr_colors(2) = "Red" arr_colors(3) = "Green" arr_colors(4) = "Orange" 'Message box shows all array items with linebreak For Each item In arr_colors CollAll = CollAll & vbNewLine & item Next item MsgBox CollAll End Sub
Result:
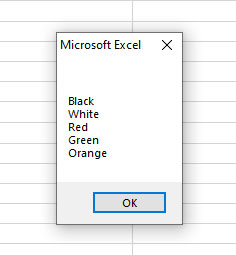
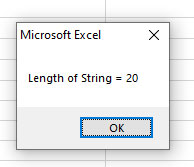
Using LBound and UBound functions to get array length
You may use LBound and UBound functions to get array length as shown in the example below.
Array length of one-dimensional array by UBound function:
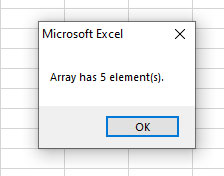
Sub Arrays_ex() Dim arr_colors(5) As String 'Creating array elements arr_colors(0) = "Black" arr_colors(1) = "White" arr_colors(4) = "Orange" 'Display Array Length MsgBox "Array has " & UBound(arr_colors) & " element(s)." End Sub
Output:
An example of creating a 2D array based on Excel cells
This is how a two-dimensional array is declared in VBA:
Or with “To”
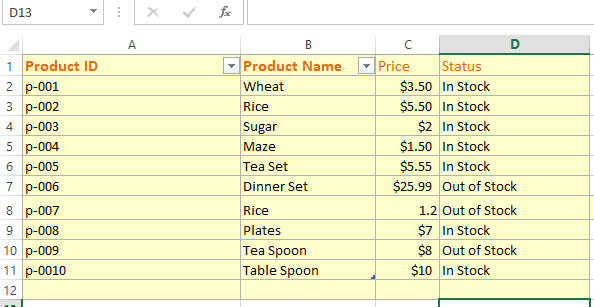
Using Excel sheet to create a 2D array:
Sample Data in our sheet
VBA Code:
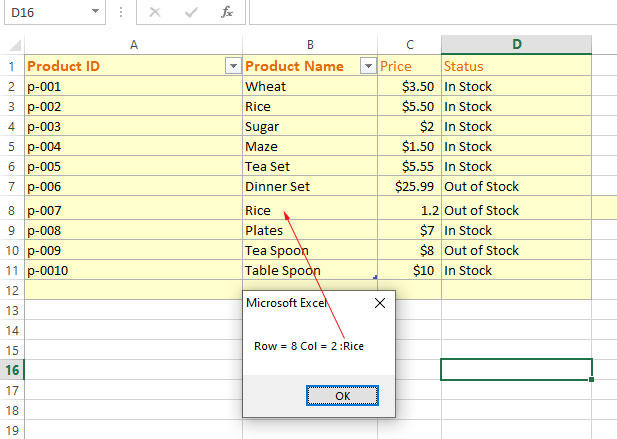
Sub Arrays_ex() 'Creating a 2D array Dim arr_products(1 To 8, 1 To 4) As String Dim x As Integer, y As Integer 'Array elements from Excel sheet For x = 1 To 8 For y = 1 To 4 arr_products(x, y) = Cells(x, y).Value Next y Next x MsgBox "Row = 8 Col = 2 :" & arr_products(8, 2) End Sub
Result:
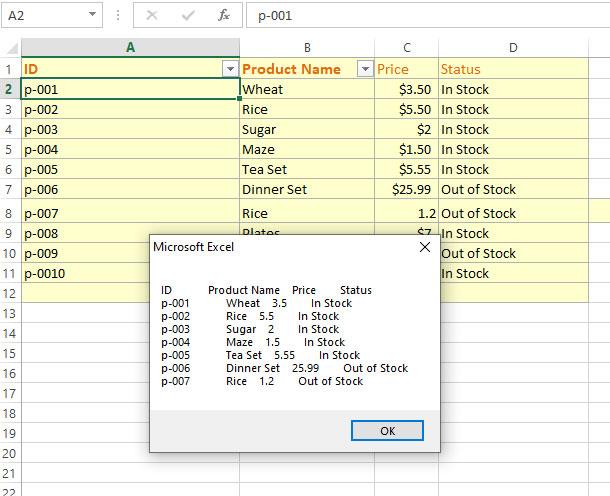
Displaying a whole two-dimensional array
Now we will display the whole array in the message box.
For that,
- We used For..Next (with inner for loop) for assigning cell values to array elements
- Another for loop is used to iterate through all 2-D array elements.
- In each iteration, we used concatenations and line breaks for better result display.
- Product ID, Names, Price, and Status are gathered in a string-type variable.
- Finally, we displayed the whole array in a message box as shown below:
VBA code:
Sub Arrays_ex() 'Creating a 2D array Dim arr_products(1 To 8, 1 To 4) As String Dim x As Integer, y As Integer 'Assigning cell values as array element values For x = 1 To 8 For y = 1 To 4 arr_products(x, y) = Cells(x, y).Value Next y Next x 'Displaying whole array in Message Box For i = 1 To UBound(arr_products) Str_Prods = Str_Prods & arr_products(i, 1) & " " & arr_products(i, 2) & " " & arr_products(i, 3) & " " & arr_products(i, 4) & vbNewLine Next i MsgBox Str_Prods End Sub
Result: